Describe the Structure and Function of the Mitotic Spindle
Cohesin holds sister chromatids together after DNA replication until anaphase when removal of cohesin leads to separation of sister chromatids. We now consider how these switches initiate such events and how the cell-cycle control system ensures that the switches fire in the correct order and only once per cell cycle.

Mechanisms And Molecules Of The Mitotic Spindle Current Biology
We begin with the two central events of the cell cycle.

. During anaphase II as in mitotic anaphase the kinetochores divide and one sister chromatid is pulled to one pole and the. Damages the mitotic spindle. The replication of DNA during S phase and.
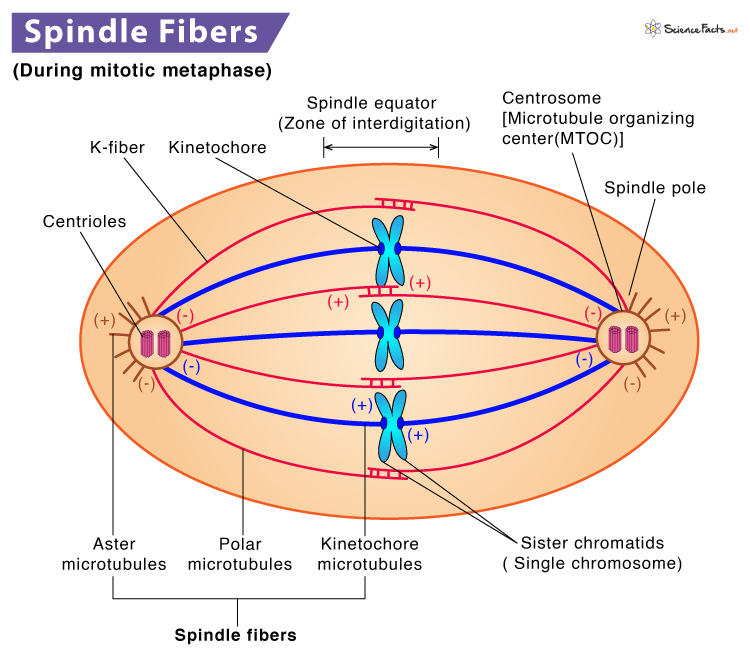
If an animal cell lacked centrioles it would not be able to. Kinetochore proteins are multiprotein complexes that bind the centromeres of a chromosome to the microtubules of the mitotic spindle. What function do centrioles perform in animal cell mitosis.
The microtubules attach at each chromosomes. Prophase During metaphase the spindle fibers form a lemon-shaped array called the _____ spindle. Two examples of chemotherapeutic drugs used to treat cancer and their cellular actions are given below.
The additional proteins at the yeast centromere attach it to the spindle microtubules and provide signals that ensure that this attachment is complete before the later stages of mitosis are allowed to proceed discussed in Chapters 17 and 18. In this case duplicated chromosomes only one set of them line up at the center of the cell with divided kinetochores attached to spindle fibers from opposite poles. In order to test this possibility we analysed the cleaning reflex as a read out for the function of the mechanosensory system of flies in conditions where the SOP mitotic wave was disrupted.
Prometaphase sees the chromosomes keep condensing while a structure called the mitotic spindle forms which is necessary to separate the chromosomes. Titin ˈ t aɪ t ɪ n also known as connectin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TTN gene. Do plant cells have centrioles.
We first describe several rare cases in which the overall structure and organization of. Each of the different cyclin-Cdk complexes serves as a molecular switch that triggers a specific cell-cycle event. Titin is a giant protein contraction for Titan protein greater than 1 µm in length that functions as a molecular spring which is responsible for the passive elasticity of muscleIt comprises 244 individually folded protein domains connected by unstructured peptide.
Microtubules grow from centrosomes placed at opposite poles of the cell. Explain why each drug could be fatal to a cell. Meiosis II is much more analogous to mitotic division.
Binds to DNA and blocks messenger RNA synthesis. In order to properly describe what happens in interphase of the cell cycle. Metaphase has the chromosomes line up at the center of the cell in between the two halves of the mitotic spindle.
The microtubules move toward the middle of the cell and attach to one of the two fused homologous chromosomes. During the mitotic phase called _____ chromosomes condense the nuclear envelope disappears spindle fibers grow and centrioles migrate to the poles of cell. Cohesin is a protein complex that mediates sister chromatid cohesion homologous recombination and DNA loopingCohesin is formed of SMC3 SMC1 SCC1 and SCC3 SA1 or SA2 in humans.
A chromosomes protein structure A primary kind of microtubule that anchors the spindle or positions the chromosome prior to mitosis A major component of the mitotic spindle. The cleaning reflex is a patterned set of leg movements elicited in a fly when its thoracic bristles receive tactile stimulation Figure 5A and Figure 5video 1. The complex forms a ring-like.

What Is A Mitotic Spindle Mitotic Spindle Formation Role Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Schematic Showing A Mitotic Spindle Inside A Cell B A Simplified 1d Download Scientific Diagram
No comments for "Describe the Structure and Function of the Mitotic Spindle"
Post a Comment